 Exercise
Exercise
Tap all the highlighted words in the text below to see their definition. ⇩SWOT and SOAR analyses are both business tools to enhance the management and strategy creation process by better understanding a business’s characteristics and opportunities.
SWOT
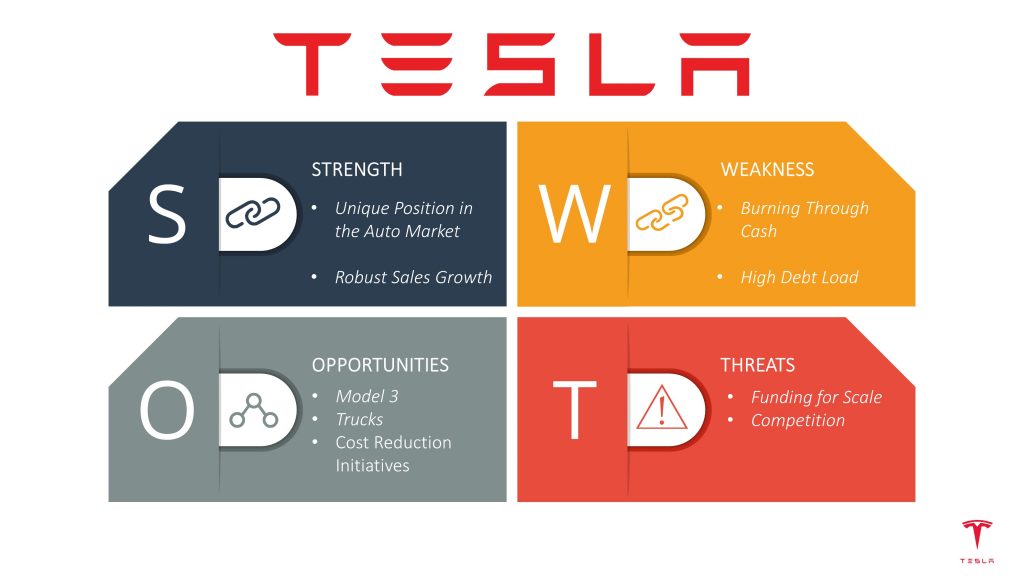
1. Strengths: These are connected to internal company elements depending on the organization. It answers the question: “What are we very good at?”. The key is to make simple lists and avoid complicated descriptions.
- E.g: A new product that nobody else is offering. (internal factor)
2. Weaknesses: These are also internal factors that depend on the organization itself. They include a simple list of all company elements that represent a weak spot compared to the market or competition. They can be connected to organization, product, process or fundings.
- E.g: We are slow in terms of internal operations. (internal factor)
3. Opportunities: We are not necessarily very good at this, but due to our situation and market conditions, we have a competitive advantage to develop this opportunity into a future strength. Since this is connected to market comparison elements, we consider it an external factor.
- E.g: Competitor lower product range could be an opportunity to increase our prices. (external factor)
4. Threats: These are based on external market factors compared to ours, but represent a menace to our business which we need to be careful with.
- E.g: A new competitor that could put us at risk. (external factor)
Let’s check another good SWOT analysis example:
SOAR
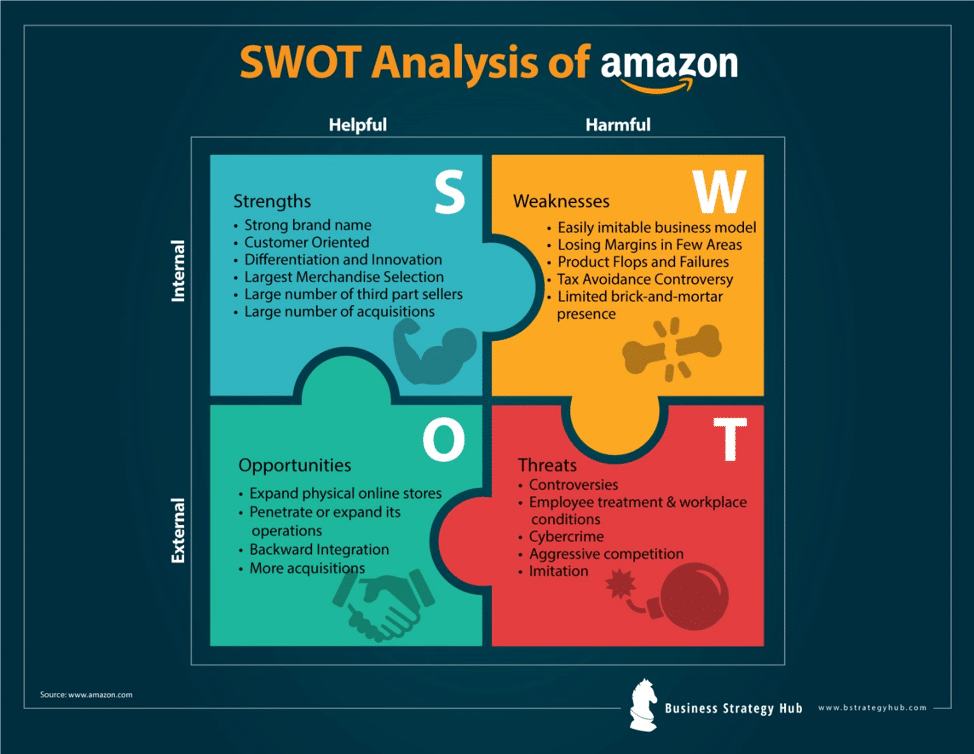
The SOAR analysis, contrary to the SWOT which focuses on weaknesses and strengths, puts all its attention into the strengths of the organization. SOAR is used for more mature organizations compared to SWOT and focuses much more on the action itself and not only the analysis.
1. Great Strengths: These are the organization elements that make you absolutely unique and the best. The driving factors to guarantee the success of the firm.
- E.g: Our very well-known brand. (external factor)
2. Opportunities: In the SOAR angle, opportunities focus on new markets or products that could be developed or improved.
- E.g: A new emerging market we can break into. (external factor)
3. Aspirations: A clear statement about what the company wants to achieve. What are our vital goals? This is very important to have a clear perspective.
- E.g: Become the number one English learning academy in the world.
4. Results: What are the simple results we expect by implementing our strategy? Increase our revenues, improve our margin. By how much? They need to be as specific as possible. Results will help you see if you are on track by implementing your strategy through concrete KPIs.
- E.g: Number of new students acquired per day.
Let’s check a good SOAR analysis example:

Well, I hope this lesson provided you with some guidance on strategic planning and clear Business English vocabulary.
Go back to unit 4 to complete all 6 microlessons.

Hi,
Good lesson,
But, I hate robot prononciation 🙁
Hi Jef, we are working to upgrade this. 🙂
Good contents. Poor narration.
Great lesson. SOAR is a new stratégic analysis concept for me. Very useful
Comparing listening to reading, there are several missing words in the written version
Thanks for your feedback, Emanuela!
Interesting
Thanks, Marcos!