 Exercise
Exercise
Tap all the highlighted words in the text below to see their definition. ⇩Introduction
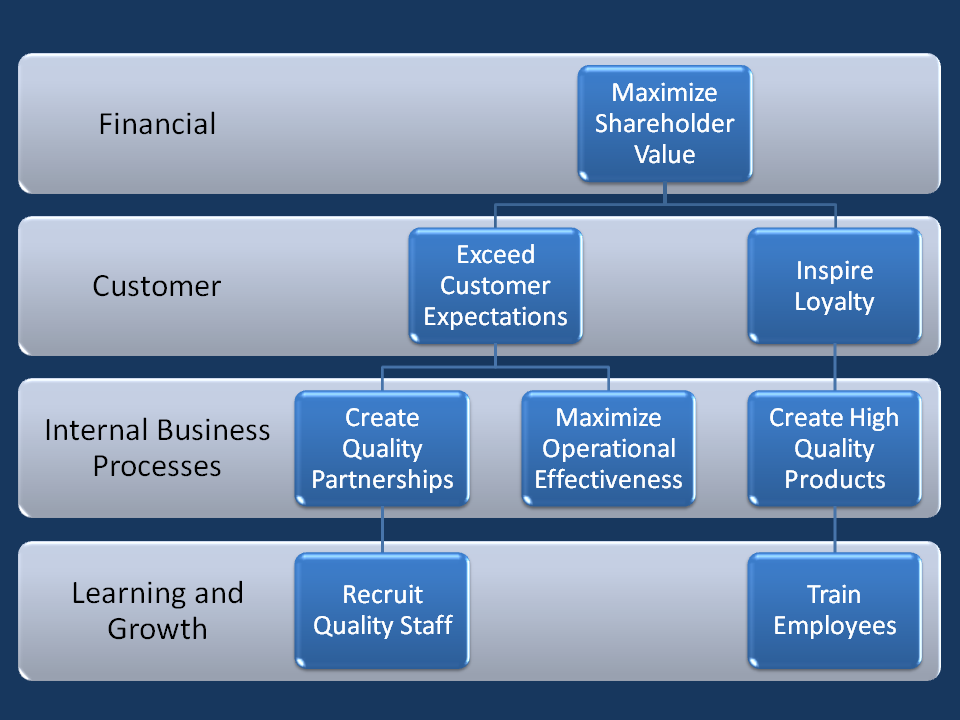
The strategy map is a visual diagram that will help you explain your strategy, priorities and positioning so everyone in the organization can easily understand. It’s created during the strategy planning process.
The structure
The strategy map gets organized around 4 main blocks or perspectives which will have concrete goals which need to be fully connected. The link between each goal from the four blocks will help you understand why each priority makes sense and if there are important missing elements of your strategy. The perspectives are:
- People & learning.
- Internal processes & operations.
- Customer perspective.
- Financial perspective.
Let’s look at some examples:
1. Learning and Growth Perspective
This is the foundation of the strategy. It outlines the employee’s skills and knowledge required to make the operations work, as well as the platform and resources that will be crucial to achieve the main goals.
2. Internal Process and Operations
This is the second layer, which explains “how” you will achieve your financial goals while dealing with clients and specific processes. Key process elements include innovation and market expansion, enhancing customer value by improving relationships with existing clients, working toward operational excellence and properly managing partner and supplier relationships.
Customer Perspective
This should describe the key factors of your customer value proposition. How are you going to differentiate yourself from your competitors while selling to customers. How will you maintain a strong and valuable relationship with them?
Financial Perspective
Upon finalising the strategy map, this details what you want to achieve financially. We can refer to revenues, margins, profits, productivity or all of them together.
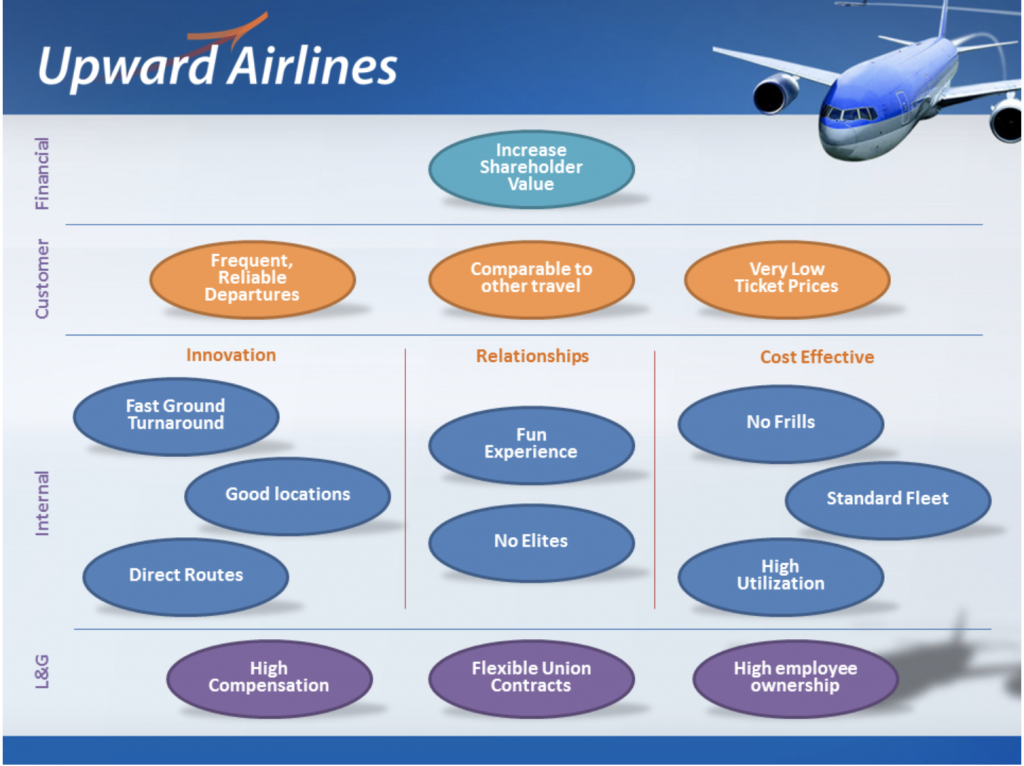
Let’s Check an Example
- Financial perspective: Achieve 100 million dollars in revenue from new clients in United States.
-
Customer perspective: Launch our new product at a lower price in the United States. -
Process perspective: Prepare our content and platform to operate in the United states. -
Internal perspective: Recruit a team to open the United States market.
Can you see? It’s very simple and practical to follow these 4 steps to design your strategy map.
Grammar – Present Simple 
See more
In the present simple all of the subjects have the same conjugation with regular verbs EXCEPT the third person singular which has an additional “-s”. That is to say that “he”, “she” and “it” have an additional “-s” at the end of their conjugations. E.g:
- I speak.
- You speak.
- He/she/it speaks.
- We speak.
- You speak.
- They speak.
Verbs which end in the following: “-ss”, “-sh”, “-ch”, “-x” and “-o” have and “-es” added to the end of the third person singular conjugation instead of an “-s”. E.g:
- He/she/it does.
The most important verbs in English “to be” and “to have” are irregular in the present tense:
- I am. / . have.
- You are. / . have.
- He/she/it is. / . has.
- We are. / . have.
- You are. / . have.
- They are. / . have.
Related Course Units
Go back to unit 4 to complete all 6 microlessons.

This is topic really good for me! Hopefully it help me to prepare some schedules
I’m glad you found it useful 🙂
Real business life
🙂
Thank you Marc, you articles are amazing and really enjoy while I learn.
very good , it s simple lecture